The abysses, covering over 70 of the Earth’s face, aren’t only vital for sustaining life but also play a pivotal part in regulating the earth’s climate. still, in recent times, the abysses have been facing an unknown trouble known as ocean acidification. This miracle, driven primarily by mortal- convinced carbon dioxide( CO2) emigrations, poses significant pitfalls to marine ecosystems and biodiversity.
Addressing ocean acidification and its consequences is imperative to guard the health of our abysses and the innumerous species that depend on them.
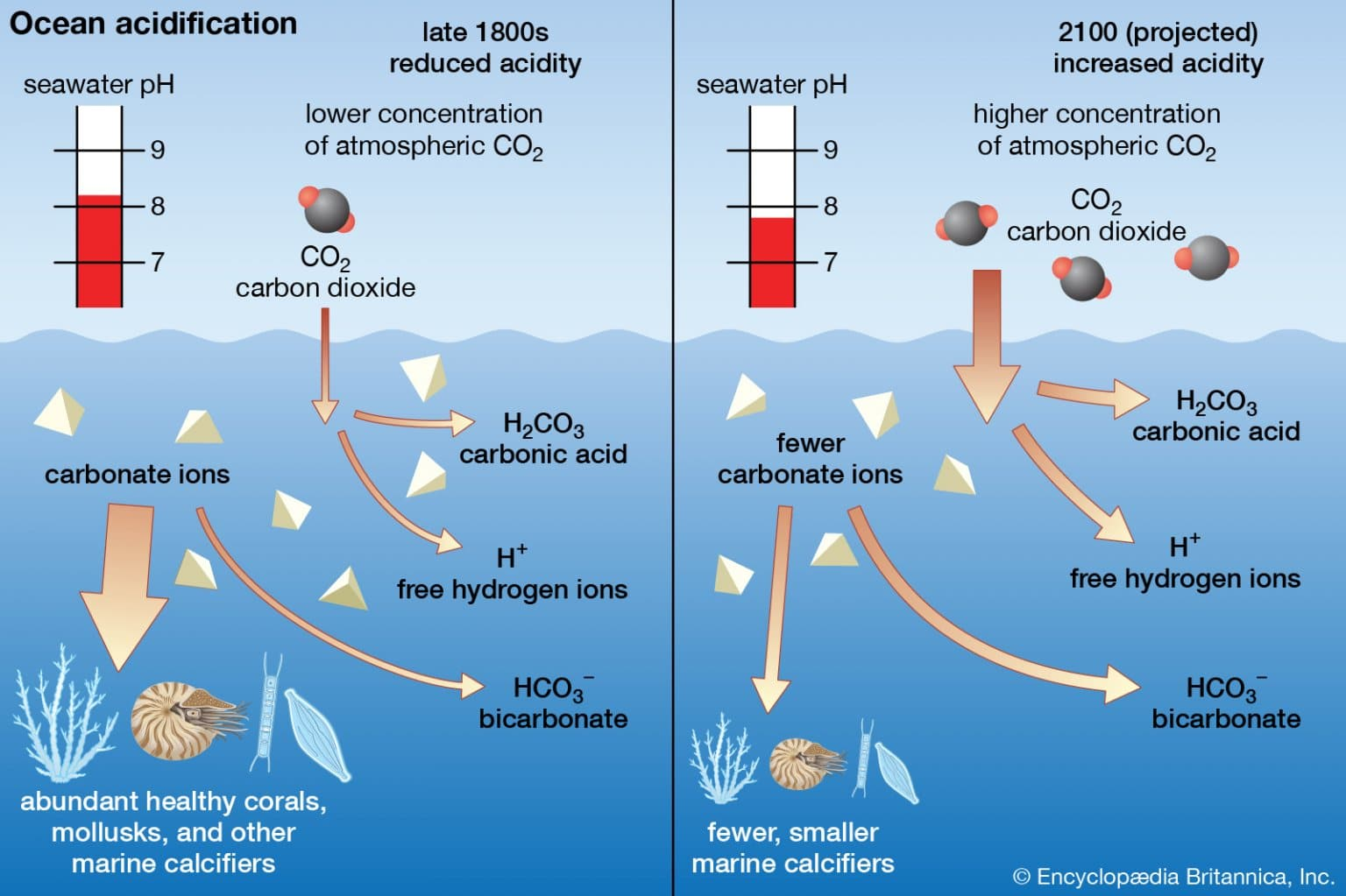
Understanding Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the process by which the pH situations of seawater drop due to the immersion of CO2 from the atmosphere. When CO2 dissolves in seawater, it forms carbonic acid, leading to a drop in pH and an increase in acidity. This change in ocean chemistry has far- reaching consequences for marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells or configurations, similar as corals, shellfish, and planktonic species.
Consequences of Ocean Acidification
Impact on Marine Life
The increased acidity of seawater hampers the capability of marine organisms to make and maintain their calcium carbonate structures. This can lead to reduced growth rates, weakened shells, and increased vulnerability to predation and complaint among shell- forming organisms like corals, mollusks, and certain species of plankton.
Dislocation of Food Chains
Ocean acidification can disrupt marine food chains and ecosystems by affecting the survival and reduplication of crucial species. For illustration, the decline of shell- forming organisms can have cascading goods on bloodsuckers and prey, leading to changes in species composition and distribution throughout marine ecosystems.
Profitable Impacts
Ocean acidification poses significant profitable pitfalls, particularly for diligence reliant on healthy marine ecosystems. Fisheries, monoculture, and tourism sectors may suffer losses due to declines in fish stocks, shellfish populations, and coral reef ecosystems, impacting livelihoods and littoral husbandry.
Pitfalls to Coral Reefs
Coral reefs, frequently appertained to as the” rainforests of the ocean,” are largely vulnerable to ocean acidification. Reduced calcification rates and coral dulling events, aggravated by warming ocean temperatures, can lead to the declination and loss of coral reef ecosystems, which are home to different marine life and give essential ecosystem services.
Addressing Ocean Acidification
Mitigating ocean acidification requires coordinated sweats at original, public, and transnational situations. Then are some crucial strategies to address this pressing issue
Addressing the root cause of ocean acidification requires global action to reduce CO2 emigrations from reactionary energy combustion, deforestation, and other mortal conditioning. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, perfecting energy effectiveness, and enforcing carbon pricing mechanisms are essential way in mollifying CO2 emigrations.
Guarding Coastal territories
Guarding and restoring littoral territories similar as mangroves, seagrass beds, and swab morasses can help cushion the impacts of ocean acidification by absorbing CO2 and furnishing niche for marine species. Conservation sweats should concentrate on conserving these critical ecosystems and enhancing their adaptability to environmental stressors.
Sustainable Fisheries Management
Implementing sustainable fisheries operation practices, similar as regulating fishing proportions, reducing bycatch, and guarding marine territories, can help maintain healthy fish populations and alleviate the impacts of ocean acidification on marine food chains.
Enhancing Research and Monitoring
Investing in scientific exploration and monitoring programs is essential for understanding the impacts of ocean acidification on marine ecosystems and relating effective mitigation strategies. Long- term monitoring sweats can track changes in ocean chemistry, biodiversity, and ecosystem health, informing adaptive operation approaches.
Promoting Ocean knowledge
Adding public mindfulness and understanding of ocean acidification and its consequences is pivotal for fostering stewardship and advocacy for ocean conservation. Education and outreach enterprise can empower individualities, communities, and decision- makers to take action to cover marine ecosystems and alleviate the impacts of ocean acidification.
Conclusion Ocean acidification poses a significant trouble to marine ecosystems, biodiversity, and the millions of people who depend on the abysses for food, livelihoods, and artistic heritage. Addressing this complex issue requires critical and combined sweats to reduce CO2 emigrations, cover littoral territories, manage fisheries sustainably, enhance exploration and monitoring, and promote ocean knowledge and stewardship. By taking decisive action to alleviate ocean acidification and its consequences, we can work towards conserving the health and adaptability of our abysses for current and unborn generations.Addressing Ocean Acidification and Its Consequences